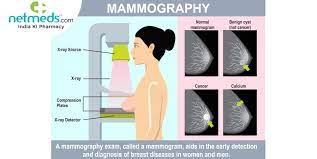
Mammography is a medical imaging technique specifically designed to examine the breast tissue. It is an essential tool for the early detection of breast cancer and is widely used as a screening method for women, particularly those who are at an increased risk of developing breast cancer.
During a mammogram, the breast is gently compressed between two plates to spread out the breast tissue. This compression is necessary for obtaining clear and detailed images.
Low-dose X-rays are used to create images of the breast tissue. Two X-ray images are typically taken of each breast: one from top to bottom and another from side to side.
Radiologists analyze the mammogram images to identify any abnormalities or suspicious areas in the breast tissue.
Using a small spatula or brush, your healthcare provider will collect cells from the surface of the cervix. This process may cause mild discomfort but should not be painful.
After the sample is collected, the speculum is removed.
Mammograms can detect breast cancer at an early stage, often before any symptoms are noticeable. Early detection is crucial because it increases the chances of successful treatment and improves overall survival rates.
Mammography is widely used as a screening tool for breast cancer. Screening mammograms are recommended for women who do not have any symptoms of breast cancer and are typically done annually or as recommended by a healthcare provider.
Mammography is also used for diagnostic purposes when a woman has symptoms or signs of breast cancer, such as a lump or nipple discharge. It can help confirm or rule out the presence of cancer. Additionally, it may be used to monitor the progression of the disease in individuals already diagnosed with breast cancer.
Mammograms can assist healthcare providers in assessing a woman’s breast cancer risk based on factors such as breast density and the presence of calcifications or masses.
If a mammogram shows an abnormality, further testing may be required, such as additional imaging (e.g., ultrasound or MRI) or a breast biopsy to determine if cancer is present.
The guidelines for mammography screening can vary based on factors like age, family history, and individual risk factors. However, in general:
It’s important to remember that mammography is a valuable tool for breast cancer detection, but it may not detect all cases of breast cancer. Therefore, it’s essential to combine regular mammograms with breast self-exams and clinical breast exams by a healthcare provider as part of a comprehensive breast health strategy. If you have questions about mammography or breast cancer screening, consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
WhatsApp us