A Pap smear, also known as a Pap test, is a screening procedure used to detect abnormal cells in the cervix, which is the lower part of the uterus (womb) that connects to the vagina. The purpose of a Pap smear is to identify early signs of cervical cancer or changes that may lead to cancer. This test can be a crucial tool in preventing cervical cancer and ensuring women’s reproductive health.
Before the test, it’s generally recommended to avoid the following for at least 48 hours:
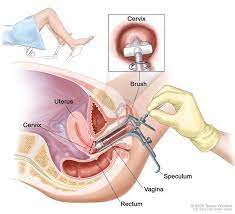
You will lie on an examination table, usually with your feet in stirrups, to allow your healthcare provider better access to the cervix.
our healthcare provider will gently insert a speculum into the vagina. The speculum is a device that holds the vaginal walls open, allowing them to see the cervix clearly.
Using a small spatula or brush, your healthcare provider will collect cells from the surface of the cervix. This process may cause mild discomfort but should not be painful.
After the sample is collected, the speculum is removed.
The collected cell samples are sent to a laboratory for analysis. There, they are examined under a microscope to identify any abnormalities.
No abnormal cells are found, and no further action is needed until the next scheduled screening.
If abnormal cells are detected, further evaluation may be necessary. This can include additional tests, such as a colposcopy, which provides a closer look at the cervix, or a biopsy to confirm the presence of abnormal cells.
It’s important to note that an abnormal Pap smear does not necessarily mean you have cervical cancer. Many times, it indicates changes in cervical cells that can be managed or treated before they progress to cancer. Early detection through regular Pap smears is essential for preventing cervical cancer or catching it at an early and highly treatable stage.
The frequency of Pap smears varies by age and individual risk factors, so it’s crucial to discuss the recommended screening schedule with your healthcare provider. Generally, routine Pap smears are recommended for most women starting around the age of 21 and continuing at regular intervals as advised by your healthcare provider.
WhatsApp us