Menopause is a natural biological process that marks the end of a woman’s reproductive years. It typically occurs in the late 40s or early 50s, although the timing can vary. Menopause is characterized by the cessation of menstruation and a decline in hormone production.
This is the transitional phase leading up to menopause. It can start several years before the final menstrual period and is marked by fluctuating hormone levels. Women may experience irregular periods, hot flashes, mood swings, and other symptoms during this phase.
Menopause is officially diagnosed after 12 consecutive months without a menstrual period. It typically occurs around the age of 51, but the age of onset can vary widely.
Postmenopause refers to the years after menopause. Symptoms such as hot flashes and mood swings may persist but usually diminish over time. Women are no longer fertile during postmenopause.
Using a small spatula or brush, your healthcare provider will collect cells from the surface of the cervix. This process may cause mild discomfort but should not be painful.
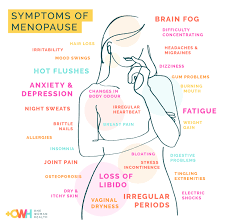
Sudden, intense feelings of heat, often accompanied by sweating and rapid heartbeat.
Hot flashes that occur during sleep, leading to night sweats and disrupted sleep patterns.
Changes in menstrual cycle length and flow, often leading to missed periods or heavy bleeding.
Reduced vaginal lubrication, which can lead to discomfort or pain during intercourse.
Mood changes, irritability, and increased risk of anxiety and depression.
Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, often linked to night sweats.
A shift in body composition and metabolism can lead to weight gain, particularly around the abdominal area.
A decrease in estrogen levels can lead to decreased bone density and an increased risk of osteoporosis.
HRT involves taking estrogen or a combination of estrogen and progestin to alleviate menopausal symptoms. It can be taken in various forms, including pills, patches, creams, or vaginal rings. HRT can also help prevent bone loss. However, it’s essential to discuss the potential benefits and risks of HRT with a healthcare provider.
Certain medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), may help manage hot flashes and mood swings.
Making healthy lifestyle changes can reduce the severity of menopausal symptoms. These include:
Over-the-counter or prescription vaginal moisturizers and lubricants can alleviate vaginal dryness and discomfort during intercourse.
Talk to your healthcare provider about bone density tests and supplements like calcium and vitamin D to support bone health.
Continue to have regular checkups with your healthcare provider to monitor your overall health and discuss any concerns or treatment options.
It’s important to remember that menopause is a natural part of the aging process, and the experience can vary greatly from person to person. Some women may have few or no symptoms, while others may find menopause challenging. Seeking guidance and support from a healthcare provider is crucial for managing menopausal symptoms and maintaining overall well-being during this life transition.
WhatsApp us